Linux
명령어
명령어 중간중간 옵션으로 -oo 붙이는건 파라미터라 부름
mkdir: 디렉토리 생성-p, --parents를 붙이면 최종 폴더를 생성하기 위해 필요하면 그 부모 폴더도 함께 생성한다.mkdir -p dir1/dir2/dir3/dir43이 없는 경우 에러가 발생.dir3폴더를 생성한다.
하지만 해당 옵션이 있으면 dir1
pwd: 현재 디렉토리ls: 현재 디렉토리 파일 보기-a: 숨겨진 파일까지 모두 보기- 숨김파일들은 파일/폴더명 앞에 .이 붙는다 (.gitignore)
-l: 자세히 보기 (파일에 대한 추가 정보 출력)-S: 파일 사이즈 기준 정렬
cd (폴더명)또는 .. : 디렉토리 이동 / ..은 뒤로가기- 폴더명 앞글자만 적고 Tab키로 자동완성 가능
cd ~는 바로 홈 디렉토리로 보내준다.
clear터미널 초기화rm (옵션) (파일명): 해당 파일 삭제-r: 해당하는 디렉토리와 그 안의 파일까지모두 삭제
touch (파일명): 파일 생성- 파일 다중 생성
touch {1..10}.md // 이름이 1~10인 md 파일이 생성된다.
- 파일 다중 생성
vi (파일명): 파일 생성 후 vim 편집기 실행cat (파일명): 파일 내용을 출력cat만 실행시키면, 사용자가 키보드로 입력하는 정보를 받아 그대로 출력. Ctrl + D로 빠져나옴.
cp (파일명) (디렉토리/새 파일명): 파일을 해당 디렉토리에 새 파일명을 지정해 복사mv (파일명) (디렉토리/새 파일명): 파일을 해당 디렉토리에 새 파일명으로 이동 (파일명을 변경할때에도 사용한다.)man (명령어): 명령어에 대한 메뉴얼 페이지로 이동 ( --help 보다 디테일한 설명)- 매뉴얼이 켜진 상태에서 특정 단어만 찾고싶을 때, '/sort' 입력
- 특정 단어가 하이라이트 되면 N키로 다음 단어로 스크롤 이동 할 수 있다.
- Q 키로 매뉴얼 빠져나감
sudo (super user do): 슈퍼유저 / 루트 권한을 사용- sudo apt-get install git : git 설치
grep (찾으려는 단어) (파일명): 파일에서 지정한 단어가 포함된 행만을 화면에 표시ps: 현재 실행되고 있는 프로세스 출력head(파일명) : 파일의 앞 10줄만 출력-n(줄 수) : 줄 수 만큼만 출력head -n2 linux.txt // linux.txt 파일의 첫 두 줄만 출력
whereis (프로그램 이름): 프로그램이 설치되어있는 위치를 출력# whereis htop htop: /usr/bin/htop
파라미터
(명령어) --help : 해당 명령어에 대한 도움말
root@goorm:/workspace/linux# rm --help 사용법: rm [<옵션>]... [<파일>]... Remove (unlink) the FILE(s). -f, --force ignore nonexistent files and arguments, never prompt -i prompt before every removal -I prompt once before removing more than three files, or when removing recursively; less intrusive than -i, while still giving protection against most mistakes --interactive[=WHEN] prompt according to WHEN: never, once (-I), or always (-i); without WHEN, prompt always --one-file-system when removing a hierarchy recursively, skip any directory that is on a file system different from that of the corresponding command line argument --no-preserve-root do not treat '/' specially --preserve-root do not remove '/' (default) -r, -R, --recursive remove directories and their contents recursively -d, --dir remove empty directories -v, --verbose explain what is being done --help 이 도움말을 표시하고 끝냅니다 --version 버전 정보를 출력하고 끝냅니다
ls -l 파일 출력 정보
파일권한 파일 소유자 크기 파일생성시간 파일이름
-rw-rw-r-- 1 root root 0 8월 8 05:46 empty_file.txt
drwxrwxr-x 2 root root 4096 8월 8 05:42 hello_linux파일 권한 앞에 d가 붙어있으면 directory라는 뜻
파일 다운로드
wget -O (파일명 지정) (파일 url)git 소스코드 다운로드
깃 설치 후
git clone http://github.com/facebook/react.git react_srcreact_src 디렉토리에 해당 git url의 오픈소스가 다운로드 됨
GUI vs CLI
graphical user interface
- 가독성, 사용성 높음
- 배우기는 쉽지만 작업의 자동화가 힘듬
Command Line Interface
- 커맨드라인으로만 이루어져 있기 때문에 CPU, 메모리 자원을 적게 먹음
- heavy한 작업에 쓰임
Sequence Execution
여러 커맨드를 ;로 구분해서 입력하면 커맨드 동작이 하나하나 완료되며 순차적으로 실행됨.
pwd;mkdir why;cd why;pwd
// 실행 결과
/workspace/linux/why
/workspace/linux/why/whyPipeline
한 커맨드의 실행 결과를 다른 커맨드의 입력으로 주기.
ls의 도움말에서 sort가 포함된 행만 찾아서 또 그 안에서 file이 포함된 행을 출력
ls --help | grep sort | grep file실행중인 프로세스에서 이름에 bash가 포함된 프로세스만 출력
ps aux | grep bash
Linux file system structure
1. / – Root
Every single file and directory starts from the root directory.
Only root user has write privilege under this directory.
Please note that /root is root user’s home directory, which is not same as /.
2. /bin – User Binaries
Contains binary executables.
Common linux commands you need to use in single-user modes are located under this directory.
Commands used by all the users of the system are located here.
For example: ps, ls, ping, grep, cp.
3. /sbin – System Binaries
Just like /bin, /sbin also contains binary executables.
But, the linux commands located under this directory are used typically by system aministrator, for system maintenance purpose.
For example: iptables, reboot, fdisk, ifconfig, swapon
4. /etc – Configuration Files
Contains configuration files required by all programs.
This also contains startup and shutdown shell scripts used to start/stop individual programs.
For example: /etc/resolv.conf, /etc/logrotate.conf
5. /dev – Device Files
Contains device files.
These include terminal devices, usb, or any device attached to the system.
For example: /dev/tty1, /dev/usbmon0
6. /proc – Process Information
Contains information about system process.
This is a pseudo filesystem contains information about running process. For example: /proc/{pid} directory contains information about the process with that particular pid.
This is a virtual filesystem with text information about system resources. For example: /proc/uptime
7. /var – Variable Files
var stands for variable files.
Content of the files that are expected to grow can be found under this directory.
This includes — system log files (/var/log); packages and database files (/var/lib); emails (/var/mail); print queues (/var/spool); lock files (/var/lock); temp files needed across reboots (/var/tmp);
8. /tmp – Temporary Files
Directory that contains temporary files created by system and users.
Files under this directory are deleted when system is rebooted.
9. /usr – User Programs
Contains binaries, libraries, documentation, and source-code for second level programs.
/usr/bin contains binary files for user programs. If you can’t find a user binary under /bin, look under /usr/bin. For example: at, awk, cc, less, scp
/usr/sbin contains binary files for system administrators. If you can’t find a system binary under /sbin, look under /usr/sbin. For example: atd, cron, sshd, useradd, userdel
/usr/lib contains libraries for /usr/bin and /usr/sbin
/usr/local contains users programs that you install from source. For example, when you install apache from source, it goes under /usr/local/apache2
10. /home – Home Directories
Home directories for all users to store their personal files.
For example: /home/john, /home/nikita
11. /boot – Boot Loader Files
Contains boot loader related files.
Kernel initrd, vmlinux, grub files are located under /boot
For example: initrd.img-2.6.32-24-generic, vmlinuz-2.6.32-24-generic
12. /lib – System Libraries
Contains library files that supports the binaries located under /bin and /sbin
Library filenames are either ld* or lib.so.
For example: ld-2.11.1.so, libncurses.so.5.7
13. /opt – Optional add-on Applications
opt stands for optional.
Contains add-on applications from individual vendors.
add-on applications should be installed under either /opt/ or /opt/ sub-directory.
14. /mnt – Mount Directory
Temporary mount directory where sysadmins can mount filesystems.
15. /media – Removable Media Devices
Temporary mount directory for removable devices.
For examples, /media/cdrom for CD-ROM; /media/floppy for floppy drives; /media/cdrecorder for CD writer
16. /srv – Service Data
srv stands for service.
Contains server specific services related data.
For example, /srv/cvs contains CVS related data.
ref : https://www.thegeekstuff.com/2010/09/linux-file-system-structure/
파일 찾기
locate
locate (파일명)locate 명령어는 디렉토리를 뒤지는게 아닌, 데이터베이스를 뒤진다.
find
find (위치) -name (파일명) sudo find / -name *.log // root폴더부터 하위폴더까지 범위에서 확장자가 .log인 파일을 찾는다. root폴더는 super user 권한이 있어야 됨. find ~ -name *.log // home 디렉토리부터 찾기. // 조건에 맞는 '파일'만 찾기 (폴더는 제외됨) find ~ -type f -name *.log // 현재 폴더 이하에서 실행가능한 파일 검색 find ./ -perm /a=x // 빈 파일만 찾기 find ./ -type f -empty find ./ -type d -empty // 폴더 // ./bak 폴더 안의 *.log인 파일 모두 삭제 find ./bak/ -type f -name "*.log" -exec rm -f {} \; // 숨김 파일 찾기 find ./ -type f -name ".*" // 최근 50일 안에 수정된 파일 검색 find / -mtime 50 find / -mtime +50 –mtime -100 // 50일 ~ 100일 사이 // 최근 1시간 안에 변경된 파일 검색 find / -cmin -60 // 50 ~ 100MB 사이 파일 검색 find / -size +50M -size -100M // 특정 파일 검색 후 삭제 find / -type f -name *.mp3 -size +10M -exec rm {} \; // 10메가 이상 mp3파일ref : https://www.tecmint.com/35-practical-examples-of-linux-find-command/
whereis
실행파일의 위치를 찾아줌
$PATH
ls나 rm 등 /bin 폴더에 있는 프로그램을 어느 디렉토리에서나 사용할 수 있는 이유는, $PATH에 /bin폴더가 등록되어있기 때문이다. 이를 환경변수라 한다.
echo $PATH위 명령어를 실행하면 등록되어있는 경로가 출력된다.
Background execute
프로그램 실행 중, Ctrl + z 키를 누르면 실행중이던 프로그램은 background로 들어가고 디렉토리 화면으로 돌아온다
그리고 fg 명령어를 입력하면 다시 실행중이던 프로그램으로 돌아온다.
현재 backgound에서 동작중인 프로그램 보기
# jobs root@goorm:/workspace/linux# jobs [1] 정지됨 nano [2] 정지됨 vim [3]- 정지됨 nano [4]+ 정지됨 htop // +는 fg명령어 입력시 foreground로 돌아올 프로그램 // -는 그 다음 프로그램원하는 프로그램을 선택해 실행하고 싶으면
fg %(프로그램 번호)를 입력하면 된다.fg %2 //vim 실행 fg %1 //nano 실행프로그램 종료
kill %2 //vim 종료 kill %1 //nano 종료 // 위 명령어로 종료가 안되면 kill -9 %1 //강력프로그램을 바로 백그라운드로 실행
ls -alR / > result.txt 2> error.log & // 대충 동작이 오래걸리는 명령어 // 명령어 & 앰퍼센드를 뒤에 입력하면 백그라운드에서 동작해서 // 바로 다음 명령어를 입력할 수 있다. // 동작이 끝나면 [n] Exit 1 이라고 뜬다.
Daemon
Daemon 프로그램들은 항상 실행되고 있다는 특성을 가지고있다.
언제 사용할지 알수 없기 때문에 (Server 등)
Daemon 프로그램들이 위치하는 디렉토리
/etc/init.dapache 설치 후 실행
// 설치 sudo apt-get install apache2 // 실행 sudo service apache2 start // 실행중 여부 확인 ps aux | grep apache2 // 종료 sudo service apache2 stopDaemon으로써 실행되는 모든 프로그램은 start / stop 명령어가 존재
리눅스 실행시 자동으로 실행되게 하기
/etc경로에는 rc~로 시작하는 디렉토리가 있는데,rc3.d는CLI방식일 때,rc5.d는GUI방식일 때 사용된다.rc3.d 디렉토리에 들어가면
../init.d/apache2가 들어가있는걸 볼 수 있다.lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 17 8월 12 04:37 S01apache2 -> ../init.d/apache2 // 맨 앞의 l은 링크라는 뜻 (바로가기) // 바로가기 이름이 S로 시작하면 리눅스 부팅시 실행되는 프로그램 // K면 실행되지 않는 프로그램 // S뒤에 01, 02는 실행 우선순위 // etc/rc3.d/ 디렉토리의 S01apache2라는 이름의 바로가기는 리눅스가 CLI방식(rc3.d)으로 구동되었을때 ../init.d/apache2 프로그램이 자동으로 실행되게 한다.- 리눅스 부팅시 프로그램이 자동으로 실행되게 하려면 CLI 부팅 기준, etc/rc3.d 디렉토리에 해당 프로그램의
링크를 걸면 된다.
- 리눅스 부팅시 프로그램이 자동으로 실행되게 하려면 CLI 부팅 기준, etc/rc3.d 디렉토리에 해당 프로그램의
CRON
정기적으로 프로그램을 실행시켜줌.
ref : https://tecadmin.net/crontab-in-linux-with-20-examples-of-cron-schedule/
크론 에디터 열기
crontab -e동작 주기 설정
m h dom mon dow command // 분 10 // 매시간 10분 */1 // 1분에 한번 // 시 * // 시간과 상관없이 // 일 dom 24 // 매달 24일 ...
1분마다 현재시간을 로그에 기록
*/1 * * * * date >> date.log 2>&12>&1 는 에러를 Standard Output으로 바꿔 date.log에 함께 저장되게 한다.
1분마다 스크립트 파일 실행
```*/1 * * * * /workspace/linux/script/auto_rsync.sh
실행
sudo service cron start동작하는 cron 목록 보기
crontab -l동작되는지 감시 (tail)
tail -f date.logdate.log를 감시하다가 파일이 수정되면 자동 리프레시
Multi User
id: 현재 사용중인 계정 정보who: 현재 접속중인 계정 리스트새 계정 생성
sudo useradd -m (유저명) // -m은 해당 유저의 /home 디렉토리를 같이 생성해준다.계정 전환
su - (유저명)Ubuntu 기준 특정 유저에게 sudo 권한 할당
sudo adduser (유저명) sudo또는
sudo usermod -a -G sudo (유저명) // sudo 그룹에 해당 유저를 넣음으로써 sudo권한 할당
Permission
다른 사용자가 작성한 파일의 수정을 하는 경우
duru@goorm:/home/surimi$ echo 'ahahaha' >> test.txt -su: test.txt: Permission denied에러가 발생한다.
파일 정보
-rw-rw-r-- 1 surimi surimi 0 Aug 13 05:14 test.txt // 맨 첫글자는 type // rw-rw-r--는 access mode // surimi : owner // 두번째 surimi : grouptype
-: 기본적인 파일d: 디렉토리
access mode
9글자(rw-rw-r--)를 3개씩 3등분해서 보면,- owner의 권한 : 'rw-'
- group의 권한 : 'rw-'
- other의 권한 : 'r--'
- other는 owner와 group을 제외한 모든 사용자
문자의 의미
- r : read
- w : write
- x : execute
- - : no permission
chmod
권한을 변경하는 명령어
// other : o // owner/user : u // group : g // all : a chmod o+w (파일명) // other에 write 권한 추가 chmod o-rw (파일명) // other에 read, write 권한 제거 chmod +x (파일명) // 모든 사용자에 대해 실행 권한 부여 /bin/bash (파일명) // 으로 권한 없이 실행이 가능 chmod a=rwx (파일명) // 모든 사용자 전체 권한 허용 chmod a= (파일명) // 모든 사용자 권한 모두 제거- 8진법 권한 설정
 ```js
chmod 777 (파일명) // 모든 사용자에게 전체 권한 허용
```
```js
chmod 777 (파일명) // 모든 사용자에게 전체 권한 허용
```
- 8진법 권한 설정
- read 권한이 없는 디렉토리는 들어갈 수 없다.
- 디렉토리에 접근 권한이 없으면 그 안의 파일의 접근 권한이 있더라도 읽거나 쓸수 없다.실행 가능한 파일
nano hi.sh // .sh 확장자로 지정하지 않아도 실행은 할 수 있다.Internet
curl(url)해당 url의 html을 출력
curl ipinfo.io/ip // ip 주소 확인 사이트Shell에서 웹 브라우징
elinks 설치 & 사용
sudo apt-get install elinkselinks (url) elinks 127.0.0.1 -> apache 서버 접속
apache2 설정
nano /etc/apache2/site-enabled/000-default.conf위 경로의 파일을 확인하면
DocumentRoot의 경로가 /var/www/html 로 설정되어있다./var/www/html 경로로 들어가면 기본으로 출력되는 index.html이 존재한다.
ref : https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=4HOqQR2kUGI&list=PLuHgQVnccGMBT57a9dvEtd6OuWpugF9SH&index=51
https://linux-lxqrn.run.goorm.io/ 에 접속하면 확인 가능
서버에 접속할 경우 /var/log/apache2/access.log에서 클라이언트 정보의 확인이 가능하다.
tail -f /var/log/apache2/access.log위 코드로 로그파일이 변경될때마다 확인 가능
SSH
서버가 켜진 다른 컴퓨터에 접속해 원격 제어가 가능설치
sudo apt-get install openssh-server sudo apt-get install openssh-client실행
sudo service ssh start
클라이언트가 설치된 리눅스 기기로 서버가 켜진 다른 리눅스 기기의 ip를 입력해 접속하면 원격 제어가 된다.
ssh -p (포트) surimi@(ip주소)
Domain
Host
접속하려는 url주소가
/etc/hosts에 입력되어 있으면 DNS서버에서 도메인을 받는걸 생략한다.127.0.0.1 localhost ::1 localhost ip6-localhost ip6-loopback fe00::0 ip6-localnet ff00::0 ip6-mcastprefix ff02::1 ip6-allnodes ff02::2 ip6-allrouters 172.17.0.29 goorm 127.0.0.1 lh --> 새로 추가curl lh를 입력하면 아파치 서버의 index.html이 출력된다.
rsync
동기화 기능
설치
sudo apt-get install rsync사용
rsync -a src/ destsrc 폴더 내 모든 파일을 dest폴더에 동기화(복사)
src/에 /를 안붙이면 dest 안에 src 폴더가 복사된다.
rsync -av src/ dest
- 결과
```
root@goorm:/workspace/linux/rsync# rsync -av src/ dest
sending incremental file list
./
1.txt
2.txt
3.txt
sent 225 bytes received 76 bytes 602.00 bytes/sec
total size is 0 speedup is 0.00
```
- 파라미터
- 파라미터에 `-v`를 붙이면 동기화 정보가 출력된다.
- 파라미터 `-a`는 아카이브 모드로 동작하게 한다.
- 두 폴더의 다른 부분만 동기화가 되도록 하고
- 파일의 권한설정같은 부분도 동기화가 된다.
- `-z`는 동기화하기 위해 데이터를 전송할때 압축해서 보낸다.
- `-P`는 전송되는 상황을 progress Bar로 보여준다.네트워크를 이용한 동기화
rsync -azP /workspace/linux/rsync/ surimi@127.0.0.1:~/rsync하고 surimi 계정의 비밀번호를 입력하면,
/workspace/linux/rsync/ 경로의 모든 파일을
127.0.0.1 주소의 surimi 계정의 ~/rsync 경로에 동기화포트가 다른 ssh에 접속할때
rsync -rvz -e 'ssh -p 58451' --progress /workspace/linux/rsync/ surimi@54.180.119.182:~/rsync
ssh 공개키 / 비공개키를 이용한 ssh 접속 로그인
키 생성
ssh-keygen위 코드를 실행해 키 생성을 마치면 ~ 디렉토리에 .ssh 폴더가 생성된다.
.ssh 폴더 안을 보면
drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 8월 13 10:59 . drwx------ 9 root root 4096 8월 13 10:54 .. -rw------- 1 root root 400 10월 22 2018 authorized_keys -rw------- 1 root root 1679 8월 13 10:59 id_rsa -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 392 8월 13 10:59 id_rsa.pub -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 444 8월 13 10:39 known_hostsid_rsa (private key)와 id_rsa.pub (public key)가 생성되어 있다.
공개키를 접속하려는 다른 리눅스 컴퓨터의 authorized_keys에 복사
ssh-copy-id surimi@127.0.0.1하고 surimi 계정의 비밀번호 입력하면 surimi 계정으로 ssh 공개키가 복사된다.
surimi@127.0.0.1에 접속을 시도하면 surimi는 authorized_keys에 담긴 key와 접속을 시도하는 계정의 rsa key를 이용한 인증 절차를 거쳐 통과하게 되면 비밀번호 입력 없이 원격 접속이 가능하게 된다.
ssh surimi@127.0.0.1ssh 자동 로그인의 장점
rsync -azP /workspace/linux/rsync/ surimi@127.0.0.1:~/rsync위 명령어는 원래 surimi@127.0.0.1에 접속하기 위해서 비밀번호를 입력해야했지만 surimi 계정의 authorized_key에 본 계정의 rsa 공개키를 입력해두었기 때문에 비밀번호 입력 절차가 생략된다.
즉, cron을 이용해 주기적으로 자동 동기화를 시킬수 있게 된다.
RSA
RSA는 비대칭성을 가진 암호화 방식
ref : https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=lLdQAIXXcMs&list=PLuHgQVnccGMBT57a9dvEtd6OuWpugF9SH&index=66
포트포워딩
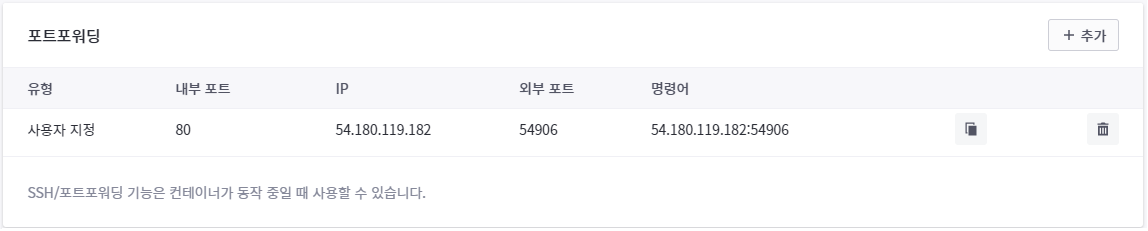
해당 ip의 외부포트로 접속하면 내부포트로 연결해준다.
아파치 서버의 내부 포트가 80일 때,
54.180.119.182:54906에 접속하면 아파치 서버로 연결된다.
'Dev > Linux' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [Goorm IDE] ssh RSA_key 접속을 못하는 상황에서 (0) | 2022.10.27 |
|---|---|
| [ Linux / bash / zsh ] 텍스트의 앞 뒤 줄을 생략하고 중간만 출력하기 (1) | 2021.12.19 |
| [Linux] Shell Script (0) | 2021.08.14 |
| [Linux] Package Manager (0) | 2021.08.14 |